Duration
60-150 minAnaesthesia
GeneralHospitalization
2 nightsReturn to society
14 daysConsistent weight fluctuations, aging and pregnancy could produce looseness of abdominal skin and excess of cutaneous - subcutaneous tissue. This condition is able to seriously impair the everyday life, sexual activity and sports.
Abdominoplasty or “tummy tuck” procedure aims to:
- remove the excess of abdominal skin and fat
- eventually repair any defect in the abdominal wall, including diasthasis of the recti abdominis muscles (the abdominal muscles could be weakened or separated)
- eventually repair small hernias of the abdominal wall
In severe cases, when the excess of skin and fat is consistent, the procedure could be extended to the whole trunk, including the posterior surface. In this case the procedure is called circumferential abdominoplasty.
In milder cases, a partial abdominoplasty (or mini-abdominoplasty) could be indicated. This procedure is less invasive and produces smaller incisions.
Abdominoplasty, as mentioned before, could be associated to ancillary procedures:
- Liposuction (lipo-abdominoplasty). This procedure allows to remove localized fat and re-contour the abdominal profile.
- Repair of the abdominal muscles. Weight loss and pregnancy could weaken and separate the recti abdomen muscles. This issue alters the contour of the abdominal wall, creates a convex deformity and increases the risk of herniation. During abdominoplasty, the surgeon can repair this weakness and dilatation, restoring a normal contour and function of the abdominal wall.
- Hernia repair (hernioplasty). Hernia is a bulging of internal organ through the wall that usually contains that organ. Weight loss and pregnancies are often associated with weakness of the abdominal wall, thus leading to the formation of hernias. When hernias are small they can be corrected during abdominoplasty.
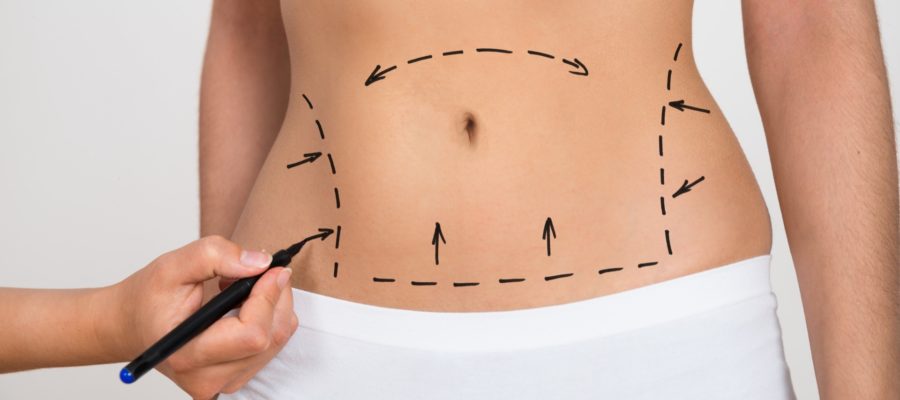
Scars of abdominoplasty are localized:
- From hip to hip just above the pubis. The scar is performed ideally under the upper level of the slip. The scar is shorter in mini-abdominoplasty (limited to the pubic area) or longer in circumferential abdominoplasty (extended to the whole trunk circumferentially)
- Around the navel. During a standard abdominoplasty a large amount of skin and adipose tissue is removed. Navel is therefore preserved and repositioned during the procedure. The repositioning could not be necessary during mini-abdominoplasty: in fact the little resection of tissue performed do not usually dislocate the navel.
Surgery is performed under general anesthesia and requires one to three hours depending on the procedure (mini-abdominoplasty, abdominoplasty or circumferential abdominoplasty). Two drains are usually introduced during surgery and should be kept in place for a variable period ranging from 2 to 7 days after surgery. Drains consist in tubes of soft silicone and their removal is painless.
The patient is required to stay in bed for 1 or 2 days depending on the amount of removed tissue. An abdominal sheath should be worn for about 30 days.
The postoperative pain is generally limited to the first 72 hours and it is more intense when repairs of the abdominal wall have been performed. Return to daily activities is allowed 14 days after surgery. Sports and physical efforts are allowed 40 days after surgery.